The History
In 1960's, after so many research, the
world's first CT scanner was invented. The inventor was Godfrey Newbold
Hounsfield, who was born in England 1919. He and Alan Cormack, a medical
physicist, together developed and placed the first brain scanner into operation
in 1971 for a company called EMI Ltd. Hounsfield conceived his idea in
1967 In 1979, they were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine and
physiology. The first EMI-Scanner was installed in Atkinson Morley Hospital in Wimbledon,
England, and the first patient brain-scan was done on 1 October 1971. It was
publicly announced in 1972.
Left; Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield
Right; Alan McLeod Cormack
The original 1971 prototype took 160 parallel readings through 180
angles, each 1° apart, with each scan taking a little over 5 minutes. The
images from these scans took 2.5 hours to be processed by algebraic
reconstruction techniques on a large computer. The scanner had
a single photomultiplier detector, and operated on the Translate/Rotate
principle.
The first production X-ray CT machine (in fact called the
"EMI-Scanner") was limited to making tomographic sections of the
brain, but acquired the image data in about 4 minutes (scanning two adjacent
slices), and the computation time (using a Data General Nova minicomputer) was about 7
minutes per picture. This scanner required the use of a water-filled Perspex tank with a pre-shaped rubber
"head-cap" at the front, which enclosed the patient's head. The
water-tank was used to reduce the dynamic range of the radiation reaching the
detectors (between scanning outside the head compared with scanning through the
bone of the skull). The images were relatively low resolution, being composed
of a matrix of only 80 × 80 pixels.
In the U.S., the first installation was at the Mayo Clinic. As a tribute to the impact of this
system on medical imaging the Mayo Clinic has an EMI scanner on display in the
Radiology Department. Allan McLeod Cormack of Tufts University in Massachusetts independently invented a
similar process, and both Hounsfield and
Cormack shared the 1979 Nobel
Prize in Medicine.
The first CT system that could make images of any part of the body and
did not require the "water tank" was the ACTA (Automatic Computerized
Transverse Axial) scanner designed by Robert S. Ledley, DDS, at Georgetown University.
This machine had 30 photomultiplier tubes as detectors and completed a scan in
only nine translate/rotate cycles, much faster than the EMI-Scanner. It used
a DEC PDP11/34 minicomputer both to operate the
servo-mechanisms and to acquire and process the images. The Pfizer drug company acquired the prototype from the
university, along with rights to manufacture it. Pfizer then began making
copies of the prototype, calling it the "200FS" (FS meaning Fast
Scan), which were selling as fast as they could make them. This unit produced
images in a 256×256 matrix, with much better definition than the EMI-Scanner's
80×80.
Since the first CT scanner, CT technology has vastly improved.
Improvements in speed, slice count, and image quality have been the major focus
primarily for cardiac imaging. Scanners now produce images much faster and with
higher resolution enabling doctors to diagnose patients more accurately and
perform medical procedures with greater precision. In the late 1990s CT
scanners broke into two major groups, "Fixed CT" and "Portable
CT". "Fixed CT Scanners" are large, require a dedicated power
supply, electrical closet, HVAC system, a separate workstation room, and a
large lead lined room. "Fixed CT Scanners" can also be mounted inside
large tractor trailers and driven from site to site and are known as
"Mobile CT Scanners". "Portable CT Scanners" are
lightweight, small, and mounted on wheels. These scanners often have built-in
lead shielding and run off of batteries or standard wall power.
In 2008 Siemens introduced a new generation of scanner that was able to
take an image in less than 1 second, fast enough to produce clear images of
beating hearts and coronary arteries.
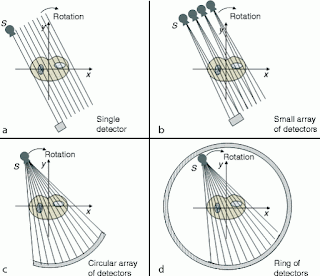
Generations of CT Scanner
|
There
are four generation of CT Scanner. In the first and second generation
designs, the X-ray beam was not wide enough to cover the entire width of the
'slice' of interest.
A
mechanical arrangement was required to move the X-ray source and detector
horizontally across the field of view.
After a
sweep, the source/detector assembly would be rotated a few degrees, and
another sweep performed.
This
process would be repeated until 360 degrees (or 180 degrees) had been
covered. The complex motion placed a limit on the minimum scan time at
approximately 20 seconds per image.
In the
3rd and 4th generation designs, the X-ray beam is able to cover the entire
field of view of the scanner. This avoids the need for any horizontal
motion; an entire 'line' can be captured in an instant. This allowed
simplification of the motion to rotation of the X-ray source.
|
The a, b, c and d images are the x-ray beam
distribution of 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th generation of CT scanner respectively.
First generation
Second generation
Third generation
Fourth generation
|


Affordable Kodak Alaris Scanner in UAE, Alaris S2070 Scanner in UAE, Scanner in UAE Visit now https://gccgamers.com/kodak-alaris-s2070-scanner-s2070.html
ReplyDeletenice post well written
ReplyDeleteEasybook Mylab is offering CT scan at best cost to nearby CT scan centre in Bangalore
Hey thегe and Thank you so much for sharing this information. It has very useful. Please keep sharing.If you want more about the best treatment for PET CT Scan, Kindly click the link
ReplyDeletepet CT scan hospital in coimbatore
Thanks for your post which is truly informative for us and we will surely keep visiting this website.
ReplyDeleteBest Diagnostic center in Hyderabad
Blood test at home
Best Radiology center in Hyderabad